For 40 years, we've been driving our country's economic and social progress. Four decades shaping Spain.
Noise Reduction
Noise Reduction
Power lines generate low-level noise in their immediate vicinity. For sub-stations, the noise can be heard at distances of up to 200 or 300 metres. We actively work to minimise this.

We measure and prevent
We comply with legislation. All our facilities are below the legal limits for exposure to the general population, either due to their location or the measures applied. However, we conduct acoustic reports before operation and acoustic simulations once operational. Although noise levels in existing facilities are below the limits, the technological advancements in new machines reduce these values by 5 to 10 dBA.
We plan
With predictions and acoustic reports prior to launching operation of the facilities and simulations to estimate the noise once the facilities are operational.
We measure
We conduct measurements to check the noise levels of our lines and sub-stations when deemed necessary. Due to urban growth, sub-stations have been surrounded by housing, which has sometimes caused inconvenience to new neighbours moving into an area close to existing facilities.
We correct
We promote innovation and R&D&I in our projects to reduce our impact in all areas. Additionally, where necessary, we implement corrective measures such as noise-absorbing acoustic screens, enclosing the power machines of sub-stations close to residential areas. Transformer sub-stations generate more noise than other facilities. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the sound pressure levels around them.
How do we correct?
- We install acoustic screens around the power equipment.
- We install silencers on the fans.
- • We listen to the public: When justified, measurements requested through the ‘Dígame’, service are carried out to confirm that the existing values are within legal limits.
These are voluntary measures that we are not obliged to take, but they form part of our commitment to society.
Noise from power lines is generated by the corona effect and is only audible in the immediate vicinity of very high-voltage lines. It is usually of low intensity and increases slightly in conditions of high ambient humidity.
The corona effect, which produces the noise, is the ionisation of the air surrounding the conductors when the electrical gradient exceeds the dielectric strength of the air. This effect manifests as small discharges a few centimetres from the cables. It is a low intensity sound that, in many cases, is barely perceptible. It is only heard in the immediate vicinity of very high-voltage lines and is not detectable from tens of metres away.
When relative humidity is high, such as when it is raining, the corona effect becomes more widespread, reaching maximum sound emission. However, in most cases, this noise is masked by the rain itself, which generates a higher noise level. The estimated sound levels when it rains at 15, 30, 50, and 100 metres from the average plane of the line do not exceed 46, 45, 43, and 38 dB(A) respectively.
When there is fog, despite the humidity, noise propagation is slowed by the presence of the fog, making it more audible near the line but undetectable at shorter distances.
In good weather, 25 metres from a 400kV line, noise levels are around 30dBA.
In sub-stations, the sound pressure levels are higher in the immediate vicinity, which is why these facilities are located far from inhabited areas.
When power machines, such as transformers or reactors, are present, sound pressure levels in the immediate vicinity of the machines range from 75-80 dB(A) with the fans off to around 80-85 dB(A) with the fans running, measured at a distance of 1 metre. Newer machines are becoming less noisy, and these values can be reduced by up to 5 dBA depending on the type of machine, manufacturer, technology, etc.
These values diminish with distance, which is why these facilities are located far from inhabited areas.
Do you want to know more about noise and health?
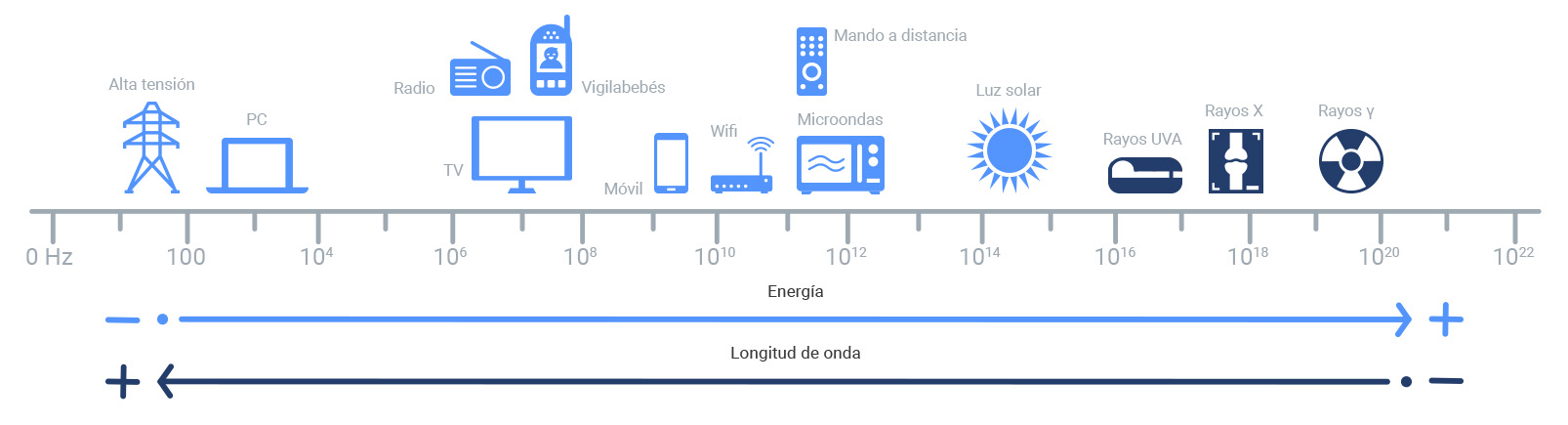
(Available only in Spanish)
Noise is detected in the ear, and it is produced by the vibration of particles which propagates through the air. This may be any unwanted sound. It is the most common pollutant and can be defined as any sound perceived by the recipient as annoying, unwanted, unwelcome, or unpleasant.
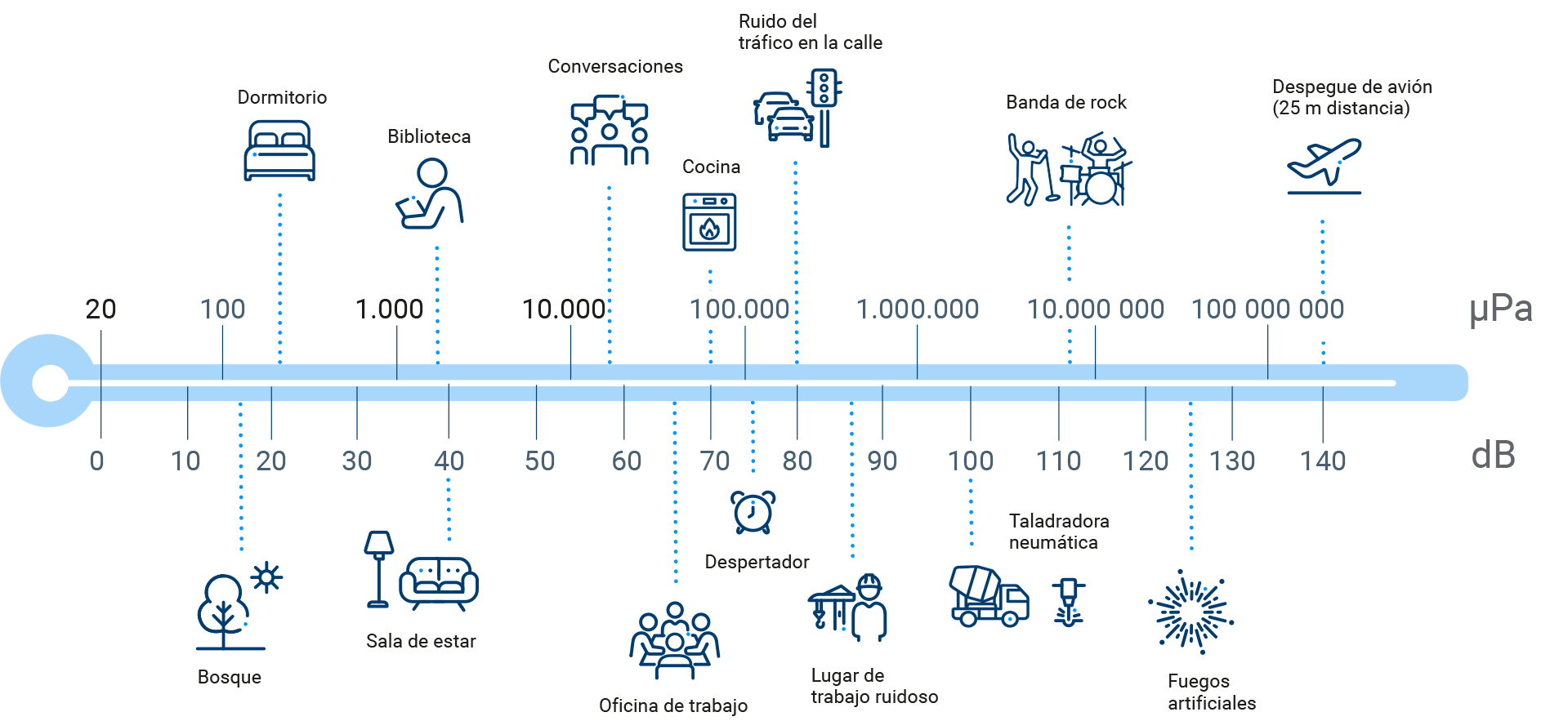
(Available only in Spanish)
There are different types of noise, such as point source noise (e.g., a person talking or a drill) and line source noise (e.g., a road with traffic, a pipe with liquid in it, or a power line).
Point source noise: Small compared to the distance to the listener. It occurs when energy propagates spherically under free-field conditions. It is reduced by 6dB when the distance to a sub-station doubles.
Line source noise: Narrow in one direction and elongated in the other. It occurs when energy propagates cylindrically under free-field conditions. It is reduced by 3dB when the distance doubles.
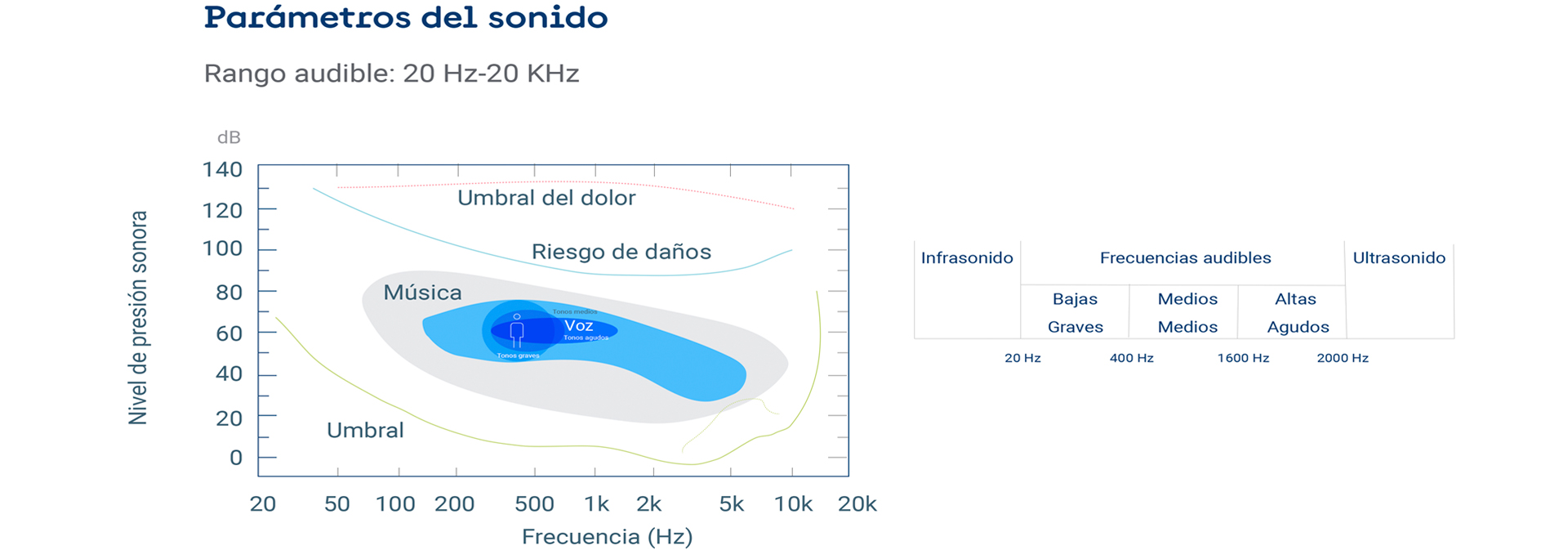
(Available only in Spanish)
Noise causes various health effects, which depend both on the level of noise and on the conditions of the receiver.
It can have direct and indirect effects. Direct effects include discomfort, nervousness, sleep disturbance, arrhythmia, respiratory disorders, and high blood pressure. Indirect or collateral effects include irritability, tiredness, aggressiveness, stomach aches, and headaches, among others.












